Table of Contents
Introduction
If you’re new to the world of coding and development, you’ve likely heard the terms Git and GitHub. But what exactly are they, and how can they benefit you? This beginner-friendly guide will introduce you to the basics of Git and GitHub, essential tools for version control and collaborative coding.
In this blog, we’ll cover the essentials of Git and GitHub, including how to get started, key features, and why they are crucial for modern development. Whether you’re a beginner looking to learn the basics or a developer aiming to refine your skills, this guide will help you understand and leverage these powerful tools.
What is Git?
Git is an open-source, distributed version control system that allows developers to track changes in their codebase, collaborate with team members, and manage different versions of their projects. It helps developers keep track of the history of changes made to their code, making it easier to revert back to previous versions if needed. Think of Git as a way to save snapshots of your work at different stages of development.
Here are some key features of Git:
- Version Control: Git keeps a history of all changes made to a project, allowing developers to revert to previous versions if needed.
- Collaboration: Multiple developers can work on the same project simultaneously without overwriting each other’s changes.
- Branching and Merging: Developers can create branches to experiment with new features or fixes independently of the main codebase, and later merge them back when they are ready.
- Distributed System: Each developer has a complete copy of the project repository, including its entire history, ensuring redundancy and data safety.
- Performance: Git is optimized for performance, handling large projects efficiently with minimal overhead.
- Repository (Repo): Think of a repository as a folder that houses your project files along with a comprehensive history of changes made to those files.
- Commit: A commit represents a snapshot of your project at a specific moment in time, capturing a set of alterations made to your files.
Git Installation Guide
Installing Git on your computer is a simple process that can be done in a few easy steps. You can start by visiting the official Git website and downloading the appropriate version for your operating system. Once downloaded, follow the installation instructions provided to set up Git on your machine.
What is GitHub?
GitHub is a popular web platform that makes software development easier and more collaborative. It’s built around Git, a tool for tracking changes in code. GitHub provides a central place where developers can store their code, making it accessible to others for collaboration and feedback. It offers features like pull requests for proposing changes, issue tracking for managing tasks and bugs, and tools for reviewing code and automating workflows. GitHub is widely used for both open-source projects and private team collaborations, providing a streamlined environment where developers can work together effectively to build and improve software.
Key Features of GitHub
- Remote Repositories: GitHub hosts your Git repositories in the cloud, providing accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection, and fostering seamless collaboration among team members.
- Pull Requests: Pull requests serve as a mechanism for proposing and reviewing changes to a repository, enabling developers to discuss, review, and refine code modifications before merging them into the main branch.
- Issues: GitHub’s issue tracker facilitates bug reporting, feature requests, and task management, serving as a centralized hub for project communication and organization.
- GitHub Actions: GitHub Actions automate workflow processes, enabling tasks such as building, testing, and deploying code directly from your GitHub repository, enhancing productivity and reducing errors.
Differences Between Git and GitHub
While Git and GitHub are closely related, they serve different purposes in the software development ecosystem:
– Git: A version control system that tracks changes in code locally on your machine.
– GitHub: A cloud platform that hosts Git repositories, enables collaboration, and offers additional tools for project management.
| GIT | GITHUB |
| Git is a software. | GitHub is a service. |
| Git is open-source licensed. | GitHub includes a free-tier and pay-for-use tier. |
| Git is a command-line tool | GitHub is a graphical user interface |
| Git is installed locally on the system. | GitHub is hosted on the web. |
| Git is focused on version control and code sharing. | GitHub is focused on centralized source code hosting. |
| Git is a version control system to manage source code history. | GitHub is a hosting service for Git repositories. |
| Git competes with CVS, Azure DevOps Server, Subversion, Mercurial, etc. | GitHub competes with GitLab, Bit Bucket, AWS Code Commit, etc. |
Git provides the core version control functionalities locally on a developer’s machine, GitHub extends Git’s capabilities by offering a centralized platform for hosting repositories, enhancing collaboration, and providing tools for project management and community engagement. Together, Git and GitHub form a powerful ecosystem that supports modern software development practices, enabling teams to work efficiently, collaborate effectively, and build high-quality software projects. Understanding the differences and synergies between Git and GitHub is crucial for developers and teams looking to leverage these tools effectively in their development workflows.
Git and GitHubWorkflow
The typical Git workflow involves creating a new repository, adding files to the repository, committing changes, and pushing those changes to a remote repository. Developers can also create branches to work on different features simultaneously, merge branches, and resolve conflicts. Git provides powerful tools for managing code development efficiently.
Git follows a simple workflow that includes four essential steps:
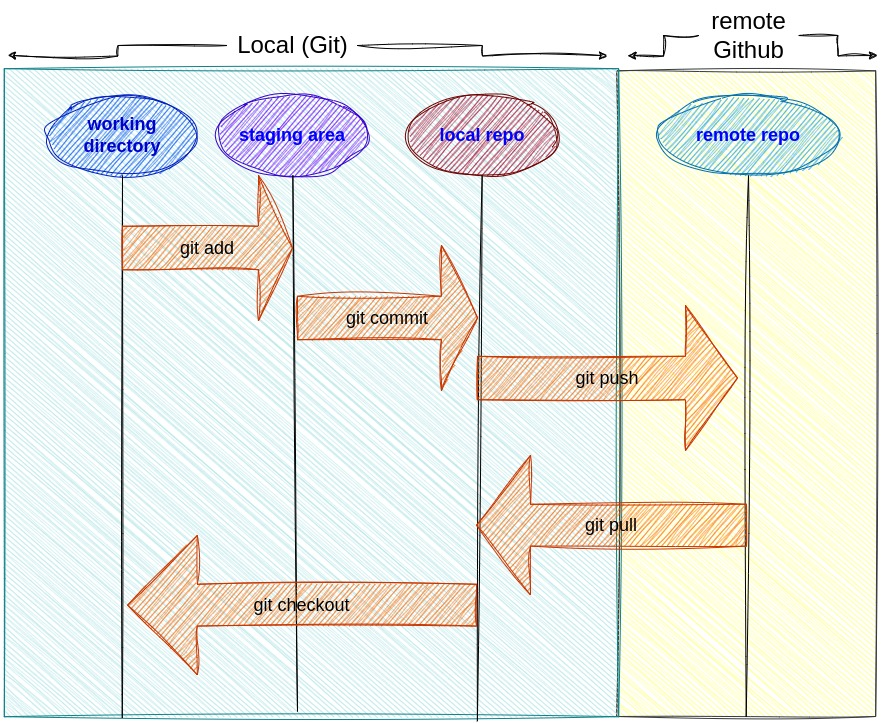
- Working Directory: This is where you modify files in your project.
- Staging Area: The staging area allows you to selectively choose which changes you want to include in the next commit. This means you can prepare a set of changes (or snapshot) before actually committing them to the Git repository.
- Local Repository: Commits are saved in the local repository on your machine.
- Remote Repository: Changes can be pushed to a remote repository, like GitHub, to collaborate with others.
Git commands
here are some commonly used Git commands along with their usage and examples:
1. git init: The git init command is used to create a new Git repository. When you run this command, Git sets up the necessary structures and files in the current directory, allowing you to start tracking changes.
The command creates a hidden directory named .git in your project’s root directory. This directory contains all the metadata and object files that Git uses to manage the repository.
git init
2. git clone: Creates a copy of an existing Git repository. Cloning is the most common way for developers to obtain a working copy of a central repository.
git clone https://github.com/username/repository.git
3. git add: Stage changes for the next commit. Moves changes from the working directory to the staging area. This gives you the opportunity to prepare a snapshot before committing it to the official history.
git add file.txt #Stage a specific file
git add # Stage all changes in the current directory
4. git commit: Takes the staged snapshot and commits it to the project history. Combined with git add, this defines the basic workflow for all Git users.
git commit -m "Add new feature"
5. git status: Show the current state of the repository.
git status
6. git pull: Pulling is the automated version of git fetch. It downloads a branch from a remote repository, then immediately merges it into the current branch.
git pull origin main
7. git push: Push local changes to the remote repository.
git push origin main
8. git branch: This command is your general-purpose branch administration tool. It lets you create isolated development environments within a single repository
git branch # List all branches
git branch # Create a new branch
git branch -d # Delete a branch
git branch # Create a new branch
git branch -d # Delete a branch
9. git checkout: Switch branches or restore working tree files. means to navigate existing branches. Combined with the basic Git commands, it’s a way to work on a particular line of development.
git checkout main # Switch to the main branch
git checkout -b # Create and switch to a new branch
10. git merge: Merge changes from one branch into another.
git checkout main # Switch to the branch you want to merge into
git merge new-feature # Merge changes from new-feature branch into main
11. git log: Display commit history.
git log
12. git remote: List all remote repositories associated with the current repository
git remote -v # List remote repositories
13. Git clean: Removes untracked files from the working directory.
git clean
Conclusion
Understanding the role of Git and GitHub is fundamental for modern software development practices. By leveraging Git for version control and utilizing GitHub for collaboration and project management, developers can streamline their workflows, foster teamwork, and build robust applications. Embrace the power of Git and GitHub to enhance your coding experience and elevate your projects to new heights.
TRENDING OFFER

